TryHackMe - Reversing ELF | Reversing
Task 1: Crackme1
Let’s start with a basic warmup, can you run the binary?
Solution
Using the following command, I was able to make the given ELF file crackme1 executable and retrieve the flag.
// Linux command
$ chmod +x crackme1
$ ./crackme1
flag
Task 2: Crackme2
Find the super-secret password! and use it to obtain the flag
Solution
After making the given file carackme2 executable, I was prompted to enter a password following the file name. Using the strings command, I was able to find the password.
// Linux command
$ chmod +x crackme2
$ strings crackme2
$ ./crackme2 super_secret_password
flag
Task 3: Crackme3
Use basic reverse engineering skills to obtain the flag
Solution
Using the strings command once more, I was able to find a base64 encoded string and I found the flag after decoding it.
// Linux command
$ chmod +x crackme3
$ strings crackme3
$ echo "base64_encoded_string_here" | base64 -d
flag
Task 4: Crackme4
Analyze and find the password for the binary?
Solution
I find it easier to use radare2 for this challenge. aaa is one of the three stages used to analyze binary and find strings and funcitons afl is used to list all of the functions; I found the main function here pdf @”function” is used to look into a specific function; I found compare.pwd which is used to compare two strings
// Linux command
$ r2 -d crackme4
$ aaa
$ afl
0x00400540 1 41 entry0
0x00400510 1 6 sym.imp.__libc_start_main
0x00400570 4 41 sym.deregister_tm_clones
0x004005a0 4 57 sym.register_tm_clones
0x004005e0 3 28 sym.__do_global_dtors_aux
0x00400600 4 45 -> 42 entry.init0
0x004007d0 1 2 sym.__libc_csu_fini
0x0040062d 4 77 sym.get_pwd
0x004007d4 1 9 sym._fini
0x0040067a 6 156 sym.compare_pwd
0x00400760 4 101 sym.__libc_csu_init
0x00400716 4 74 main <------------------ This is the "main" function
0x004004b0 3 26 sym._init
0x00400530 1 6 loc.imp.__gmon_start__
0x004004e0 1 6 sym.imp.puts
0x004004f0 1 6 sym.imp.__stack_chk_fail
0x00400500 1 6 sym.imp.printf
0x00400520 1 6 sym.imp.strcmp
$ pdf@main
; DATA XREF from entry0 @ 0x40055d
┌ 74: int main (int argc, char **argv, char **envp);
│ ; var int64_t var_10h @ rbp-0x10
│ ; var int64_t var_4h @ rbp-0x4
│ ; arg int argc @ rdi
│ ; arg char **argv @ rsi
│ 0x00400716 55 push rbp
│ 0x00400717 4889e5 mov rbp, rsp
│ 0x0040071a 4883ec10 sub rsp, 0x10
│ 0x0040071e 897dfc mov dword [var_4h], edi ; argc
│ 0x00400721 488975f0 mov qword [var_10h], rsi ; argv
│ 0x00400725 837dfc02 cmp dword [var_4h], 2
│ ┌─< 0x00400729 741b je 0x400746
│ │ 0x0040072b 488b45f0 mov rax, qword [var_10h]
│ │ 0x0040072f 488b00 mov rax, qword [rax]
│ │ 0x00400732 4889c6 mov rsi, rax
│ │ 0x00400735 bf10084000 mov edi, str.Usage_:__s_password_nThis_time_the_string_is_hidden_and_we_used_strcmp_n ; 0x400810 ; "Usage : %s password\nThis time the string is hidden and we used strcmp\n"
│ │ 0x0040073a b800000000 mov eax, 0
│ │ 0x0040073f e8bcfdffff call sym.imp.printf ; int printf(const char *format)
│ ┌──< 0x00400744 eb13 jmp 0x400759
│ │└─> 0x00400746 488b45f0 mov rax, qword [var_10h]
│ │ 0x0040074a 4883c008 add rax, 8
│ │ 0x0040074e 488b00 mov rax, qword [rax]
│ │ 0x00400751 4889c7 mov rdi, rax
│ │ 0x00400754 e821ffffff call sym.compare_pwd <---------- It compares rdi and rax where rax is the input we put.
│ │ ; CODE XREF from main @ 0x400744
│ └──> 0x00400759 b800000000 mov eax, 0
│ 0x0040075e c9 leave
└ 0x0040075f c3 ret
$pdf@sym.compare_pwd
; CALL XREF from main @ 0x400754
┌ 156: sym.compare_pwd (int64_t arg1);
│ ; var int64_t var_28h @ rbp-0x28
│ ; var int64_t var_20h @ rbp-0x20
│ ; var int64_t var_18h @ rbp-0x18
│ ; var int64_t var_10h @ rbp-0x10
│ ; var int64_t var_eh @ rbp-0xe
│ ; var int64_t var_8h @ rbp-0x8
│ ; arg int64_t arg1 @ rdi
│ 0x0040067a 55 push rbp
│ 0x0040067b 4889e5 mov rbp, rsp
│ 0x0040067e 4883ec30 sub rsp, 0x30
│ 0x00400682 48897dd8 mov qword [var_28h], rdi ; arg1
│ 0x00400686 64488b042528. mov rax, qword fs:[0x28]
│ 0x0040068f 488945f8 mov qword [var_8h], rax
│ 0x00400693 31c0 xor eax, eax
│ 0x00400695 48b8495d7b49. movabs rax, 0x7b175614497b5d49
│ 0x0040069f 488945e0 mov qword [var_20h], rax
│ 0x004006a3 48b857414751. movabs rax, 0x547b175651474157
│ 0x004006ad 488945e8 mov qword [var_18h], rax
│ 0x004006b1 66c745f05340 mov word [var_10h], 0x4053 ; 'S@'
│ 0x004006b7 c645f200 mov byte [var_eh], 0
│ 0x004006bb 488d45e0 lea rax, [var_20h]
│ 0x004006bf 4889c7 mov rdi, rax
│ 0x004006c2 e866ffffff call sym.get_pwd
│ 0x004006c7 488b55d8 mov rdx, qword [var_28h]
│ 0x004006cb 488d45e0 lea rax, [var_20h]
│ 0x004006cf 4889d6 mov rsi, rdx
│ 0x004006d2 4889c7 mov rdi, rax
│ 0x004006d5 e846feffff call sym.imp.strcmp ; int strcmp(const char *s1, const char *s2)
│ 0x004006da 85c0 test eax, eax
│ ┌─< 0x004006dc 750c jne 0x4006ea
│ │ 0x004006de bfe8074000 mov edi, str.password_OK ; 0x4007e8 ; "password OK"
│ │ 0x004006e3 e8f8fdffff call sym.imp.puts ; int puts(const char *s)
│ ┌──< 0x004006e8 eb16 jmp 0x400700
│ │└─> 0x004006ea 488b45d8 mov rax, qword [var_28h]
│ │ 0x004006ee 4889c6 mov rsi, rax
│ │ 0x004006f1 bff4074000 mov edi, str.password___s__not_OK_n ; 0x4007f4 ; "password \"%s\" not OK\n"
│ │ 0x004006f6 b800000000 mov eax, 0
│ │ 0x004006fb e800feffff call sym.imp.printf ; int printf(const char *format)
│ │ ; CODE XREF from sym.compare_pwd @ 0x4006e8
│ └──> 0x00400700 488b45f8 mov rax, qword [var_8h]
│ 0x00400704 644833042528. xor rax, qword fs:[0x28]
│ ┌─< 0x0040070d 7405 je 0x400714
│ │ 0x0040070f e8dcfdffff call sym.imp.__stack_chk_fail ; void __stack_chk_fail(void)
│ └─> 0x00400714 c9 leave
└ 0x00400715 c3 ret
Now, I need to know what rdi is and I need to set a breakpoint at the address move rdi, rax with the command db 0x004006d2 before strcmp function is called to compare them. First, open the program in debugger mode with any argument. ood ‘anything’ Then, set a breaking point and run with dc Finally, examine the value of rdi.
// Linux command
$ood 'anything'
$db 0x004006d2
$dc
$px @rdi
- offset - 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F 0123456789ABCDEF
0x7fff24aba610 6d79 5f6d 3072 335f 7365 6375 7233 5f70 <---- Answer
0x7fff24aba620 7764 0000 0000 0000 0065 6a8c 7e63 798f .......ej.~cy.
Task 5: Crackme5
What will be the input of the file to get output Good game ?
Solution
I solved this using radare2 as well. I looked over the main function and found that _sym.strcmp__ is being called.
// Linux command
$ pdf @sym.strcmp_
...
│ 0x00400761 4889ce mov rsi, rcx
│ 0x00400764 4889c7 mov rdi, rax <----- Need to set a breaking point here.
│ 0x00400767 e8f4fdffff call sym.imp.strncmp ; int strnc
...
$ db 0x00400764
$ dc
Enter your input:
Doesn't matter what you enter here. We just want to run the program.
hit breakpoint at 0x400764
I tried viewing the content of rdi. However, it wasn’t the answer. I tried the other variables and rsi worked for me. The answer actually does show up in rdi as well, but it just wasn’t in the first two lines.
// Linux command
$ px @rsi
- offset - 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F 0123456789ABCDEF
0x7ffcbff88cf0 4f66 646c 4453 417c 3374 5862 3332 7e58 <----- Answer
0x7ffcbff88d00 3374 5840 7358 6034 7458 747a 0000 0000 ....
Task 6: Crackme6
Analyze the binary for the easy password
Solution
This time, I am using a different tool called Ghidra because it was much easier for me to understand. Whether you use Ghidra or radare2, you will come to the same conclusion that main function -> compare_pwd function -> my_secure_test function. However, Ghidra will decompile the code right away for you.
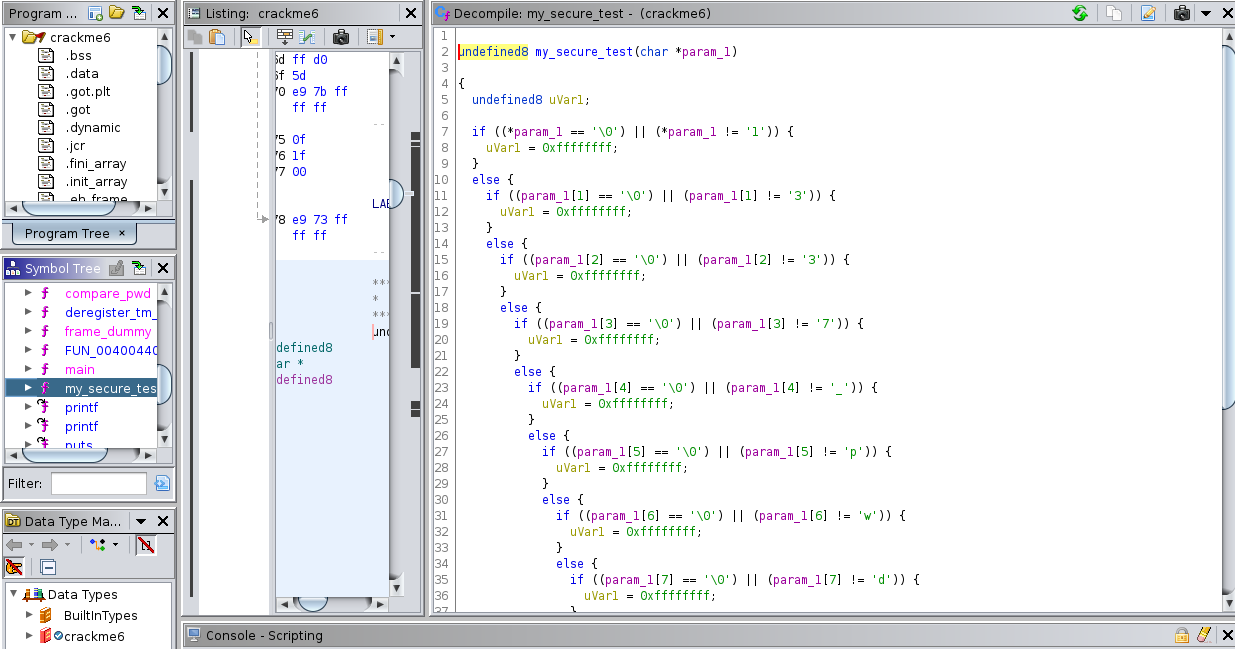
As shown in the screenshot, it’s just a bunch of if-statements that validate the input character by character.
Password = 13…..d
Task 7: Crackme7
Analyze the binary to get the flag
Solution
I will be using Ghidra for this as well. Analyzing the main function, I see that it gives the user three options to choose from. If the user answers with an unexpected option: 0x7a69, then it will call giveFlag() function. Please note that, 0x7a69 refers to its decimal form, which is 31337.
// Linux command
$ ./crackme7
Menu:
[1] Say hello
[2] Add numbers
[3] Quit
[>] 31337
Wow such h4x0r!
flag
Task 8: Crackme8
Analyze the binary to get the flag
Solution
This one was surprisingly easier than the last one. The main function basically states if the input == -0x35010ff3, which is -889262067 in decimal form, then it will call the giveFlag() function to give you the flag.
// Linux command
$ ./crackme8 -889262067
Access granted.
flag